SCS
0.0200


Researchers at Europe's science lab CERN, who regularly use particle physics to challenge our understanding of the universe, are also applying their craft to upend the limits to cancer treatment.
The physicists here are working with giant particle accelerators in search of ways to expand the reach of cancer radiation therapy, and take on hard-to-reach tumours that would otherwise have been fatal.
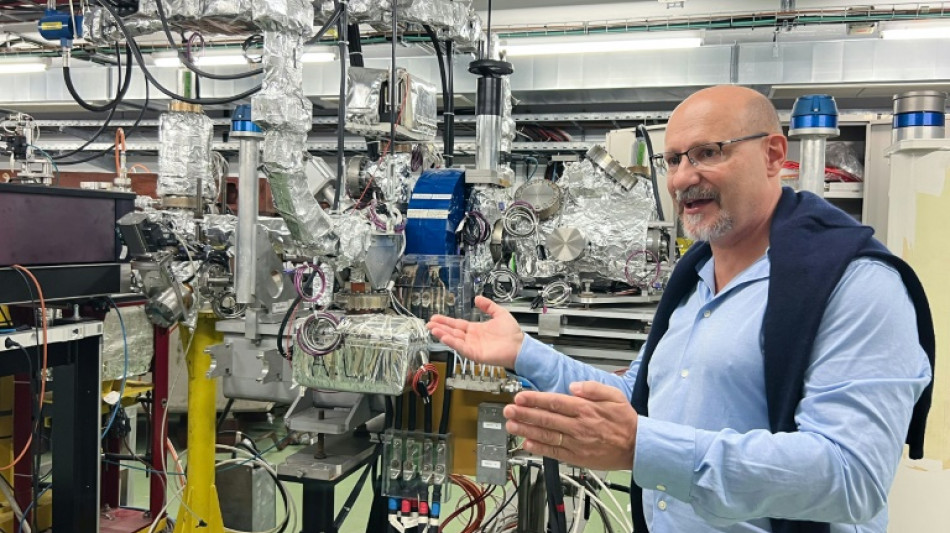
In one CERN lab, called CLEAR, facility coordinator Roberto Corsini stands next to a large, linear particle accelerator consisting of a 40-metre metal beam with tubes packed in aluminium foil at one end, and a vast array of measurement instruments and protruding colourful wires and cables.
The research here, he told AFP during a recent visit, is aimed at creating very high energy beams of electrons -- the negatively charged particles in the nucleus of an atom -- that eventually could help to combat cancerous cells more effectively.
They are researching a "technology to accelerate electrons to the energies that are needed to treat deep-seated tumours, which is above 100 million electron volts" (MeV), Corsini explained.
The idea is to use these very high energy electrons (VHEE) in combination with a new and promising treatment method called FLASH.
- Reducing 'collateral damage' -
This method entails delivering the radiation dose in a few hundred milliseconds, instead of minutes as is the current approach.
This has been shown to have the same destructive effect on the targeted tumour, but causes far less damage to the surrounding healthy tissue.
With traditional radiation therapy, "you do create some collateral damage," said Benjamin Fisch, a CERN knowledge transfer officer.
The effect of the brief but intense FLASH treatment, he told reporters, is to "reduce the toxicity to healthy tissue while still properly damaging cancer cells."
FLASH was first used on patients in 2018, based on currently available medical linear accelerators, linacs, that provide low-energy electron beams of around 6-10 MeV.
At such low energy though, the beams cannot penetrate deeply, meaning the highly-effective treatment has so far only been used on superficial tumours, found with skin cancer.
But the CERN physicists are now collaborating with the Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV) to build a machine for FLASH delivery that can accelerate electrons to 100 to 200 MeV, making it possible to use the method for much more hard-to-reach tumours.
- 'Game-changer' -
Deep-lying cancer tumours that can't be rooted out using surgery, chemotherapy or traditional radiation therapy are often today considered a death sentence.
"It is the ones which we don't cure at the moment which will be the targets," Professor Jean Bourhis, head of CHUV's radiology department, told AFP.
"For those particular cancers, which may be one third of the cancer cases, it could be a game-changer."
There are particular hopes that the FLASH method, with its far less harmful impact on surrounding tissue, could make it possible to go after tumours lodged in the brain or near other vital organs.
Bourhis said it might not relegate deaths from stubborn cancer tumours to the history books, "but at least there will be a new opportunity for more cures, if it works."
- 'Compact' -
One challenge is making the powerful accelerator compact enough to fit inside a hospital.
At CERN, a large gallery has been dedicated to housing the CLEAR accelerator, which requires 20 metres to push the electrons up to the required energy level -- and another 20 metres to condition, measure and deliver the beam.
But Corsini insisted that CERN had the know-how to "accelerate in a much more compact space".
The prototype being designed with CHUV will aim to do the same job with a machine that is 10 metres overall.
This "compact" solution, Corsini said, "reduces the cost, reduces power consumption and variability, and you can easily put it into a hospital without having to build a whole building."
Construction of the prototype is scheduled to begin next February, and patient clinical trials could begin in 2025, Bourhis said, "if everything goes smoothly".
Y.Hara--JT