SCS
0.0200


Neuroscientists have shown that lab-grown brain cells can learn to play the classic video game Pong, and could be capable of "intelligent and sentient behavior."
Brett Kagan, who led a study published in the journal Neuron Wednesday, told AFP his findings open the door to a new type of research into biological information processors, complementing normal digital computers.
"What machines can't do is learn things very quickly -- if you need a machine learning algorithm to learn something, it requires thousands of data samples," he explained.
"But if you ask a human, or train a dog, a dog can learn a trick in two or three tries."
Kagan, chief scientific officer at Melbourne-based Cortical Labs, set out to answer whether there is a way to harness the inherent intelligence of neurons.
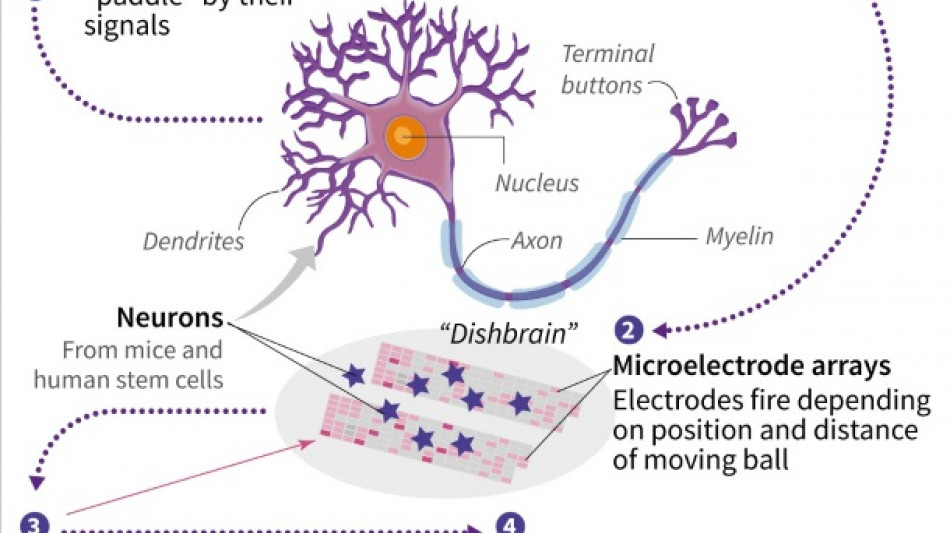
Kagan and colleagues took mice cells from embryonic brains, and derived human neurons from adult stem cells.
They then grew them on top of microelectrode arrays that could read their activity and stimulate them. The experiments involved a cluster of around 800,000 neurons, roughly the size of a bumblebee brain.
In the game, a signal was sent from the left or right of the array to indicate where the ball was located, and "DishBrain," as the researchers called it, fired back signals to move the paddle, in a simplified, opponent-free version of Pong.
- 'Sentient, but not conscious' -
One of the major hurdles was figuring out how to "teach" the neurons.
In the past, it has been proposed to give them a shot of the "feel good" hormone dopamine to reward a correct action -- but that was difficult to achieve in a time-sensitive way.
Instead, the team relied on a theory called the "free energy principle" that was coined by the paper's senior author Karl Friston, which says cells are hardwired to minimize unpredictability in their environments.
When the neurons succeeded in making the paddle hit the ball, they received "predictable" electrical signals. But when they missed, they were sent randomized, or "unpredictable" signals.
"The only thing that the neurons could do is actually get better at trying to hit the ball to keep their world controllable and predictable," said Kagan.
DishBrain's performance isn't up to AI (artificial intelligence) or human standards, but "the fact we see any significant learning is really just evidence of how robust neurons are at processing information and adapting to their environment," he added.
The team believes DishBrain is sentient -- which they defined as being able to sense and respond to sensory information in a dynamic way -- but drew the line at calling it "conscious," which implies awareness of being.
DishBrain also tried out another task -- the dinosaur game that appears in Google Chrome when no internet connection is found -- and the preliminary results were encouraging, said Kagan.
For their next steps, the team plans to test how DishBrain's intelligence is affected by medicines and alcohol -- though Kagan himself is most excited by the future possibilities of biological computers based on this discovery.
"We compare it to the first transistor," he said, the building block of modern electronics invented in 1947, which eventually led to today's powerful digital computers.
"This is robustly conducted, interesting neuroscience," said Tara Spires-Jones of the Centre for Discovery Brain Science at the University of Edinburgh, who was not involved in the study.
"Don't worry, while these dishes of neurons can change their responses based on stimulation, they are not SciFi style intelligence in a dish, these are simple (albeit interesting and scientifically important) circuit responses."
M.Yamazaki--JT