SCS
0.0200

Over the past year the Iranian economy has slid into its most severe crisis since the 1979 revolution. The national currency, the rial, has lost nearly half of its value against the United States dollar in the space of a year, with exchange rates in the open market climbing from around 817,000 rials per dollar at the start of 2025 to well over 1.4 million by the end of December. In parallel, inflation has remained above 40 per cent for several consecutive years, and the cost of staple foods has skyrocketed – bread and grains have almost doubled in price and fruit has climbed by more than 70 per cent in the past twelve months. Years of international sanctions, particularly on oil exports, have eroded government revenues and restricted access to hard currency. A multi‑tier exchange system has allowed importers linked to the political elite to buy dollars at preferential rates, reinforcing perceptions of deep economic injustice.
These structural weaknesses have been exacerbated by external shocks. A twelve‑day war with Israel in mid‑2025 damaged infrastructure across several cities and caused further economic disruption. In September 2025 the United Nations re‑imposed sanctions linked to Iran’s nuclear programme, and a new tier in the national fuel subsidy system introduced in December raised petrol prices for many households. The cumulative effect has been a sharp decline in purchasing power for ordinary Iranians and a contraction in gross domestic product that is forecast to continue through 2026.
Protests ignite across the country
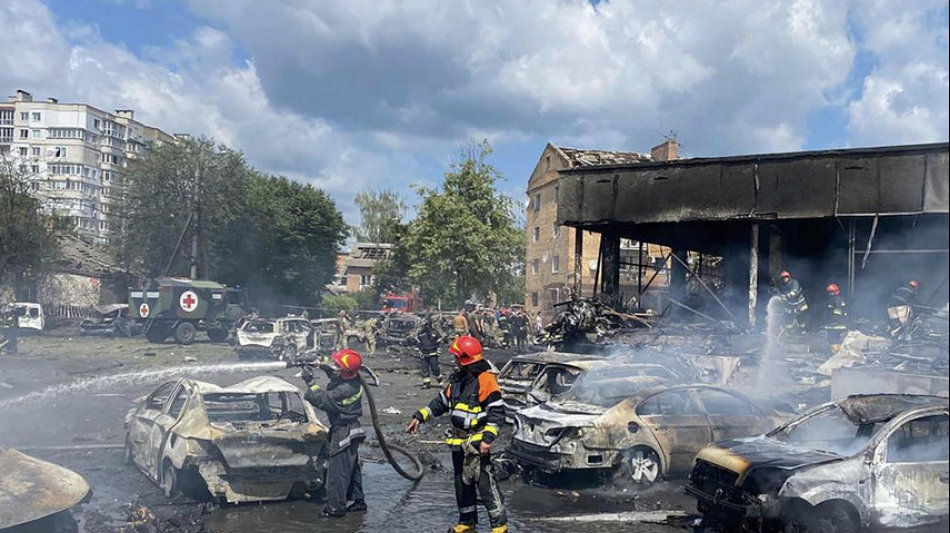
The acute deterioration in living standards reached a tipping point on 28 December 2025. Merchants and shopkeepers in Tehran’s Grand Bazaar closed their premises in protest at soaring prices and the collapsing currency. Their grievances quickly resonated with a wider cross‑section of society. Within days, demonstrations had spread to the provinces and to university campuses. Students, workers, oil sector employees and lorry drivers joined the strikes, turning an economic protest into a nationwide movement challenging the legitimacy of the Islamic Republic.
Protesters chanted slogans that harked back to Iran’s monarchical past and openly called for the resignation of key figures in the Islamic government. They denounced corruption and the dominance of the Revolutionary Guard Corps in sectors ranging from oil to construction. Anxiety about price volatility – the inability of merchants to set stable prices for imported goods – was as potent a driver as the level of inflation itself. The convergence of bazaaris, students and industrial workers signalled a new and dangerous alliance for the regime, recalling historical moments when alliances between merchants and clerics had toppled previous governments.
Government response and growing casualties
Faced with the largest challenge to its authority in years, the government of President Masoud Pezeshkian acknowledged that the crisis was self‑inflicted and promised to listen to “legitimate demands”. The central bank governor was dismissed and a monthly food coupon system was introduced to cushion the poorest households, while officials talked of institutional reforms and new subsidies to support essential goods. At the same time, security forces moved swiftly to suppress the unrest. Police and Revolutionary Guard units deployed tear gas, batons and, in some cases, live ammunition. Internet access was throttled across the country, leaving citizens cut off from one another and from the outside world.
Rights organisations estimate that thousands of protesters and members of the security forces have been killed since late December. Tens of thousands have been arrested. The authorities have not issued official casualty figures but concede that many security personnel have died. Footage circulating on social media shows large crowds chanting in support of the exiled Pahlavi heir, burning portraits of the Supreme Leader and attacking symbols of the state.
International implications and the path ahead
The turmoil has reverberated far beyond Iran’s borders. Diplomatic missions were briefly shut, and governments in Europe and North America summoned Iranian ambassadors to protest at the crackdown. The United States, which reimposed unilateral sanctions in 2018 and was involved in recent military strikes against Iran’s nuclear facilities, has warned that further violence against demonstrators could trigger intervention. Calls for the Iranian government to respect fundamental freedoms have come from allied governments and international organisations.
Internally, the protests reveal deep structural tensions within the Islamic Republic. The concentration of economic power in the Revolutionary Guard Corps has deprived elected officials of the means to manage the economy, while corruption and opaque networks of patronage have alienated the bazaar merchants who once underpinned the system. A prolonged drought, air pollution and energy shortages have further undermined the regime’s legitimacy.
Whether this wave of unrest will bring about immediate political change remains uncertain. Iran has witnessed large‑scale protests in 2009, 2017, 2019 and 2022, all of which were eventually suppressed. The current movement is remarkable for its geographic reach – demonstrations have been reported in all 31 provinces – and for the diversity of participants. However, opposition factions remain fragmented, and there is as yet no universally recognised figurehead capable of unifying the disparate groups. The security apparatus remains loyal to the Supreme Leader, and there are few signs of internal splits that could precipitate a rapid collapse of the regime.
Nevertheless, the economic crisis shows no sign of abating. With oil revenues constrained, inflation entrenched and the currency in freefall, the government’s tools for stabilisation are limited. Many Iranians believe that nothing short of a fundamental transformation of the political system will end decades of hardship. The protests of late 2025 and early 2026 may therefore mark the beginning of a new chapter in Iran’s modern history – a turning point where economic desperation accelerates the decline of a revolutionary regime that has dominated the country for almost half a century.