SCS
0.0200


US scientists have measured Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity -- which holds that gravity slows time down -- at the smallest scale ever, demonstrating that clocks tick at different rates when separated by fractions of a millimeter.
Jun Ye, of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Colorado Boulder, told AFP it was "by far" the most precise clock ever built -- and could pave the way for new discoveries in quantum mechanics, the rulebook for the subatomic world.
Ye and colleagues published their findings in the prestigious journal Nature on Wednesday, describing the engineering advances that enabled them to build a device 50 times more precise than their previous best clock, itself a record-breaker, built in 2010.
It was more than a century ago, in 1915, that Einstein put forward his theory of general relativity, which held that the gravitational field of a massive object distorts space-time.
This causes time to move more slowly as one approaches closer to the object.
But it wasn't until the invention of atomic clocks -- which keep time by detecting the transition between two energy states inside an atom exposed to a particular frequency -- that scientists could prove the theory.
Early experiments included the Gravity Probe A of 1976, which involved a spacecraft six thousand miles (10,000 kilometers) above Earth's surface and showed that an onboard clock was faster than an equivalent on Earth by one second every 73 years.
Since then, clocks have become more and more precise, and thus better able to detect the effects of relativity.
A decade ago, Ye's team set a record by observing time moving at different rates when their clock was moved 33 centimeters (just over a foot) higher.
- Theory of everything -
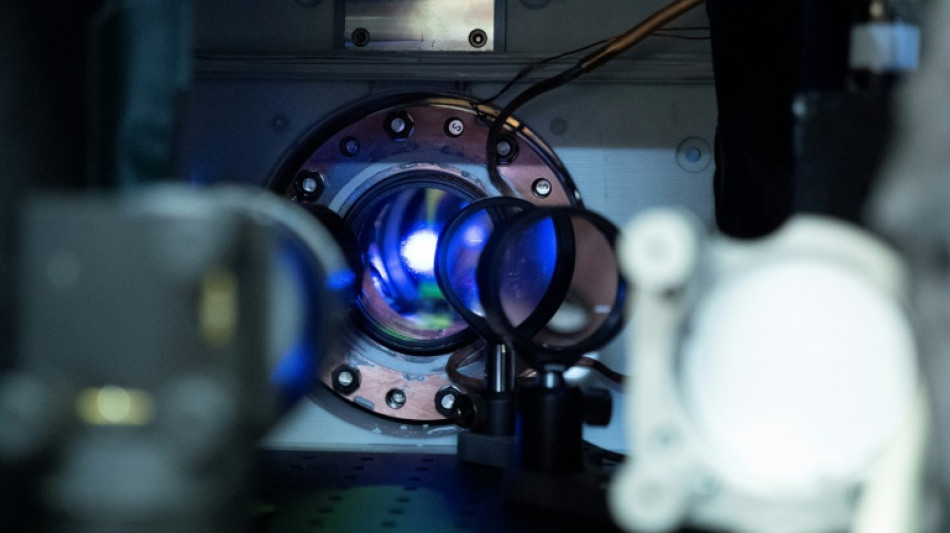
Ye's key breakthrough was working with webs of light, known as optical lattices, to trap atoms in orderly arrangements. This is to stop the atoms from falling due to gravity or otherwise moving, resulting in a loss of accuracy.
Inside Ye’s new clock are 100,000 strontium atoms, layered on top of each other like a stack of pancakes, in total about a millimeter high.
The clock is so precise that when the scientists divided the stack into two, they could detect differences in time in the top and bottom halves.
At this level of accuracy, clocks essentially act as sensors.
"Space and time are connected," said Ye. "And with time measurement so precise, you can actually see how space is changing in real time -- Earth is a lively, living body."
Such clocks spread out over a volcanically-active region could tell geologists the difference between solid rock and lava, helping predict eruptions.
Or, for example, study how global warming is causing glaciers to melt and oceans to rise.
What excites Ye most, however, is how future clocks could usher in a completely new realm of physics.
The current clock can detect time differences across 200 microns -- but if that was brought down to 20 microns, it could start to probe the quantum world, helping bridge gaps in theory.
While relativity beautifully explains how large objects like planets and galaxies behave, it is famously incompatible with quantum mechanics, which deals with the very small, and holds that everything can behave like a particle and a wave.
The intersection of the two fields would bring physics a step closer to a unifying "theory of everything" that explains all physical phenomena of the cosmos.
S.Yamamoto--JT