SCS
0.0200


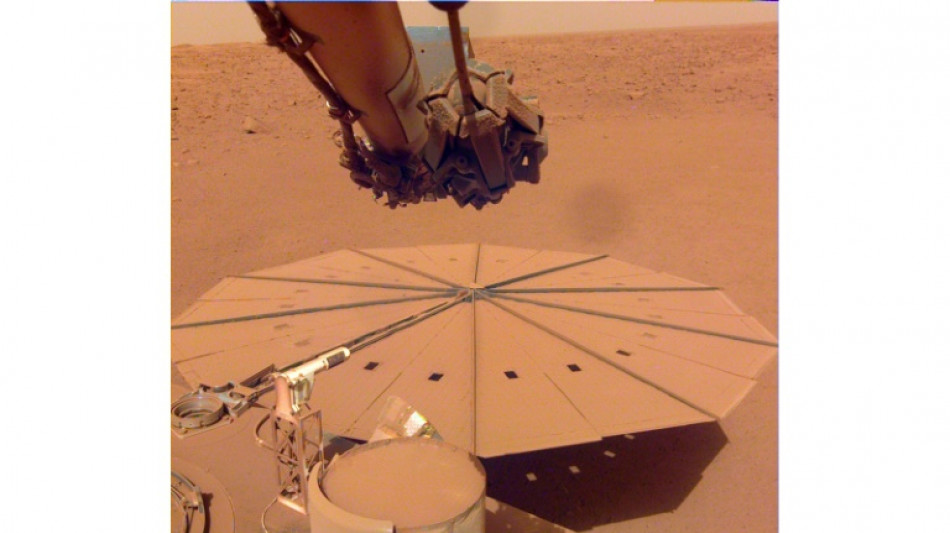
After some four years probing Mars' interior, NASA's InSight lander will likely retire this summer as accumulated dust on its solar panels saps its power.
The lander will, however, leave behind a legacy of data that will be tapped by scientists around the world for years to come, helping to improve our understanding of planet formation, NASA said, while announcing on Tuesday the imminent end to InSight's science operations.
Equiped with an ultra-sensitive seismometer, InSight recorded more than 1,300 "marsquakes," including a magnitude 5 quake on May 4, the largest so far.
But around July, the seismometer will be turned off.
The lander's energy level will then be checked about once a day, and some pictures may still be taken. Then by the end of 2022, the mission will be completely stopped.
The cause: the accumulation over months of Martian dust on the lander's two solar panels, each measuring about seven feet (2.2 meters) wide.
InSight, which is already running on only a tenth of the energy it had at the beginning, will soon find its batteries drained.
The speed at which dust accumulated corresponded more or less to what had been estimated by NASA.
The lander got a new lease on life around a year ago, when its robotic arm was put to new and unplanned use to remove some dust from the solar panels, extending the mission.
The maneuver -- employed six times successfully -- saw the arm use dust itself to clear the panels, as it scooped up some martian soil and gently dropped onto the robot so the dirt was blown across the solar panels, clearing parts of their surface.
Adding something to the lander specifically to clean the panels was forgone due to costs, explained Bruce Banerdt of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, during a press conference Tuesday.
Such a mechanism would leave "less to put into the science instruments," he said.
- 'Treasure trove' -
InSight, one of four missions currently on the Red Planet -- along with the US rovers Perseverance and Curiosity, and China's Zhurong -- arrived on Mars in November 2018.
Its seismometer, made in France, has since paved the way for great advances.
"The interior was kind of just a giant question mark," said Banerdt, who has worked on the InSight mission for more than a decade.
But thanks to InSight, "we've been able to map out the inside of Mars for the very first time in history."
Seismic waves, varying based on the materials they pass through, offer a picture of the interior of the planet.
For example, scientists were able to confirm that the core of Mars is liquid and to determine the thickness of the Martian crust -- less dense than previously thought and likely consisting of three layers.
The magnitude 5 quake in early May was much larger than all those previously recorded and close to what scientists thought would be the maximum on Mars, though it would not be considered a huge tremor on Earth.
"This quake is really going to be a treasure trove of scientific information when we get our teeth into it," Banerdt said.
Earthquakes are in particular caused by plate tectonics, he explained. But, they can also be triggered when the Earth's crust moves due to temperature anomalies caused by its mantle.
It is this type of vibration that scientists think they are dealing with on Mars.
Not all of InSight's scientific operations have gone smoothly, however, such as when its heat probe had trouble being successfully buried below the surface to take the planet's temperature because of the composition of the soil where the robot landed.
Regardless, in light of the seismometer's success, NASA is considering using the technique elsewhere in the future, said Lori Glaze, director of NASA's Planetary Science Division.
"We'd really like to set up a complete network on the moon to really understand what's going on there."
K.Yoshida--JT