SCS
0.0200


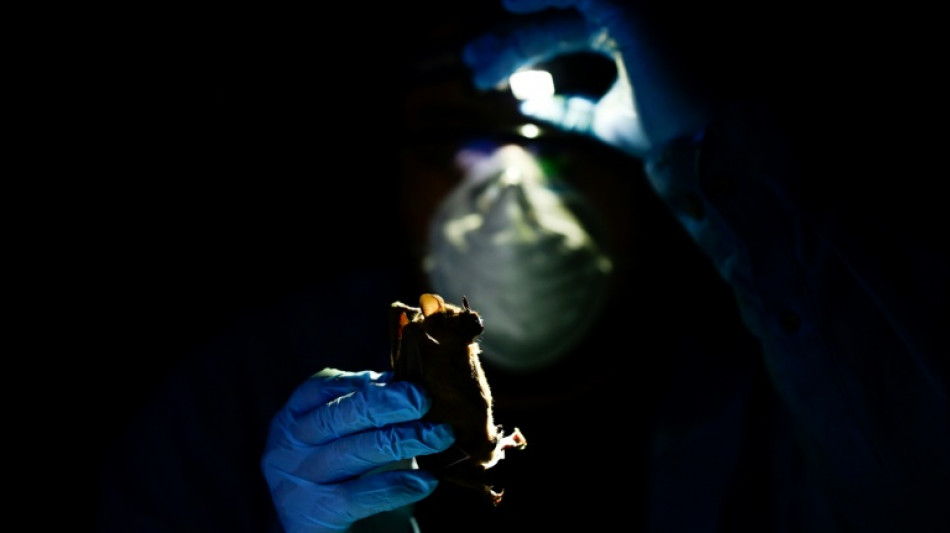
As night fell in Mexico's Yucatan jungle, veterinarian Omar Garcia extracted blood and fluids from a bat as part of an investigation aimed at preventing the next potential pandemic.
The goal of the Franco-Mexican project is to detect diseases -- known as zoonoses -- transmitted from animals to humans in tropical climates.
Bats are under scrutiny from the international scientific community as a possible source of coronavirus transmission.
The winged mammal remained immobile while bearing its fangs, before being released by Garcia, a vector-borne disease expert.
Scientists from France's Research Institute for Development (IRD) and the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) have been collaborating in the study since 2017, using a modern laboratory in Merida, the Yucatan state capital.
The aim is to discover how different viruses that circulate between animals such as mammals, birds and rodents, can potentially pass to humans, said Audrey Arnal, an infectious diseases expert at the IRD.
"This is zoonosis... understanding what the consequences of human contact with wildlife could be and then understanding what could be the next epidemic that can come out of nature," she told AFP.
Scientists take samples of all kinds of animals from the rich ecosystem of the tropical rainforest, where they have identified 61 species of mosquitoes.
"We have many questions" to try to "complete the history of the transmission cycle" of viruses, said UNAM biologist Maria Jose Tolsa, who after a decade of research finally feels that the importance of her work is recognized.
"A pandemic has serious consequences for health and the economy," she said.
- High-risk zone -
The area was chosen for the research because rapid deforestation has made it "a highly emblematic region in terms of zoonosis emergency risks," said Benjamin Roche, a specialist in ecology and evolutionary biology at the IRD.
It is estimated that between 500,000 and 800,000 viruses could affect humans, he added.
The risks grow with the expansion of agriculture and tourism, which increase contact between animals and humans, according to researchers.
Thousands of trees have been felled in the Yucatan Peninsula to build President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador's flagship tourist rail project, the Mayan Train, scheduled to start operating in December.
The government says that it is offsetting the loss with a tree-planting program and the creation of the second-largest tropical rainforest reserve in the world after the Amazon.
The key is to achieve a balance between humans and nature, Arnal said.
"The population have to live, eat and develop their economy," she added.
The research is being carried out in 12 communities across the three states that make up the Yucatan Peninsula.
"In birds we've found species that have been identified as reservoirs for the West Nile virus or influenza," said Rosa Elena Sarmiento, from the virology laboratory of the UNAM Veterinary School.
- 'Great revealer' -
Field work begins at dawn by placing a dozen fine nets to trap birds. At dusk it is the turn of bats and even owls.
Once caught, blood, fluid and ectoparasite samples -- if they carry them -- are taken.
Scientists identify the animal, measure it, record the data and check its condition before releasing it.
Later the material is analyzed in the laboratory.
"DNA is a great revealer," Arnal said.
"With the blood of the mosquito we can determine which species or which animal was bitten," she added.
Blood samples will also be taken from local residents to determine if they carry any virus that came from an animal.
The project also includes consultations with communities to learn about their environmental and social problems, and encourage forms of coexistence with nature.
"There has to be a knowledge dialogue with the communities," said Erika Marce Santos, a member of the Mexican Association of Conservation Medicine who liaises with residents.
The Merida laboratory is connected with others in Africa, South Asia and other Latin American countries within the framework of an initiative called Preventing Zoonotic Disease Emergence.
Launched by France in 2022, it brings together 22 countries and 200 organizations.
"What we're looking for in the Yucatan is to devise a prevention strategy against zoonoses that can serve as an example to the whole world," Roche said.
K.Abe--JT