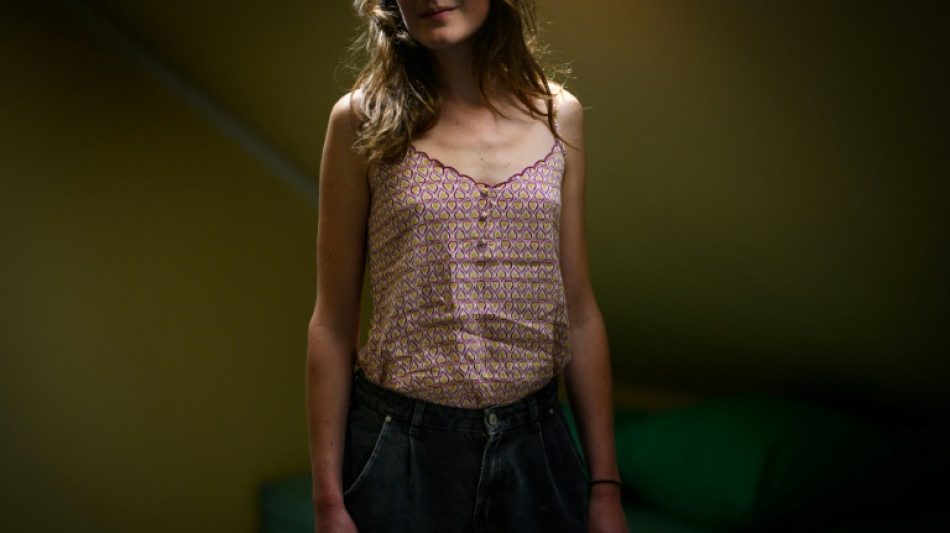
SCS
0.0200

Social media can push vulnerable young people towards developing eating disorders by glorifying thinness and promoting fake, dangerous advice about diet and nutrition, experts warn.
Young women and girls are much more likely to suffer from illnesses such as anorexia, bulimia and binge eating disorder, though rates among men have been increasing.
Research has shown the percentage of people worldwide who have had some kind of eating disorder during their lives rose from 3.5 percent in 2000 to 7.8 percent in 2018, a timeframe that captures the rise of social media.
For the professionals trying to help teenagers recover from these disorders, misinformation from influencers on platforms such as TikTok and Instagram is a huge problem.
"We no longer treat an eating disorder without also addressing social media use," French dietitian and nutritionist Carole Copti told AFP.
"It has become a trigger, definitely an accelerator and an obstacle to recovery," she added.
The causes of eating disorders are complex, with psychological, genetic, environmental and social factors all having the potential to make someone more susceptible.
Social media "is not the cause but the straw that may break the camel's back," said Nathalie Godart, a psychiatrist for children and adolescents at the Student Health Foundation of France.
By promoting thinness, strictly controlled diets and relentless exercise, social media weakens already vulnerable people and "amplifies the threat" to their health, she told AFP.
- 'Vicious cycle' -
Just one recent example is the #skinnytok trend, a hashtag on TikTok full of dangerous and guilt-inducing advice encouraging people to drastically reduce how much food they eat.
For Charlyne Buigues, a French nurse specialising in eating disorders, social media serves as a gateway to these problems, which are "normalised" online.
She condemned videos showing young girls with anorexia exposing their malnourished bodies -- or others with bulimia demonstrating their "purges".
"Taking laxatives or vomiting are presented as a perfectly legitimate way to lose weight, when actually they increase the risk of cardiac arrest," Buigues said.
Eating disorders can damage the heart, cause infertility and other health problems, and have been linked to suicidal behaviour.
Anorexia has the highest rate of death of any psychiatric disease, research has found. Eating disorders are also the second leading cause of premature death among 15- to 24-year-olds in France, according to the country's health insurance agency.
Social media creates a "vicious cycle," Copti said.
"People suffering from eating disorders often have low self-esteem. But by exposing their thinness from having anorexia on social media, they gain followers, views, likes... and this will perpetuate their problems and prolong their denial," she added.
This can especially be the case when the content earns money.
Buigues spoke of a young woman who regularly records herself throwing up live on TikTok and who had "explained that she was paid by the platform and uses that money to buy groceries".
- 'Completely indoctrinated' -
Social media also makes recovering from eating disorders "more difficult, more complicated and take longer", Copti said.
This is partly because young people tend to believe the misleading or fake diet advice that proliferates online.
Copti said consultations with her patients can feel like she is facing a trial.
"I have to constantly justify myself and fight to make them understand that no, it is not possible to have a healthy diet eating only 1,000 calories -- that is half what they need -- or that no, it is not normal to skip meals," she said.
"The patients are completely indoctrinated -- and my 45-minute weekly consultation is no match for spending hours every day on TikTok," she added.
Godart warned about the rise of people posing as "pseudo-coaches", sharing incorrect, "absurd" and potentially illegal nutrition advice.
"These influencers carry far more weight than institutions. We're constantly struggling to get simple messages across about nutrition," she said, pointing out that there are lifelines available for those in need.
Buigues takes it upon herself to regularly report problematic content on Instagram, but said it "serves no purpose".
"The content remains online and the accounts are rarely suspended -- it's very tiring," she said.
The nurse has even advised her patients to delete their social media accounts, particularly TikTok.
"It may seem radical but until young people are better informed, the app is too dangerous," she said.
M.Yamazaki--JT